| Discone Antennas | |
 |
 |
DAEMON - A small program that runs in the background on Unix and other machines while other, higher-priority, programs run in the foreground. [10:1634]
DAMAGE ASSESSMENT - See BATTLE DAMAGE ASSESSMENT
DATA ARCHEOLOGY - See DATA MINING
DATA ASSOCIATION - The process of correlating new pieces of information with other reports, targets or tracks in the data base. See also DATA COMBINATION/ FUSION/ REASONING. [5:2]
DATA COMBINATION - The (primarily) numerical process which uses the multiple sensor measurements to classify the target or event into one or more categories (friend-foe-neutral, warhead, decoy, fighter-bomber or specific target type such as the Delta class submarine). [5:2] See also DATA ASSOCIATION/ FUSION / REASONING.
DATA DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM (DDS) - That component of the COOPERATIVE ENGAGEMENT SYSTEM (CES) that collects data from the COOPERATIVE ENGAGEMENT PROCESSOR (CEP), encrypts it, and transmits it to other cooperating units (CUs). It also accepts data from the CUs and sends it to the local CES. [10:2666] See also COOPERATIVE ENGAGEMENT.
DATA DREDGING - See DATA MINING
DATA DRIVEN ATTACK - A form of attack used by CRACKERS which is characterized by its being encoded inside innocuous data which is then executed by a user or other software to implement the attack. [] See also E-MAIL BOMB, HACKER NOTE: Data driven attacks may get through the FIREWALL in data form, enabling the attack to be launched behind the firewall.
DATA FUSION - The fully automated method of merging diverse data into a single, coherent representation of the tactical, operational or strategic situation. See also DATA ASSOCIATION, DATA COMBINATION, DATA REASONING. [5:2]
DATA MINING - (1) The attempt to find patterns, especially those which are hidden an unexpected, in data. [10:2833] (2) An iterative process of extracting patterns from a set of data, such as from those in a DATA WAREHOUSE, in order to deduce implicit, previously unknown, and potentially useful information. Data mining uses machine learning, statistical and visualization techniques to discover and present knowledge in a from that can be comprehended easily by humans. [] Also called DATA ARCHEOLOGY, DATA DREDGING, DATA PATTERN PROCESSING, INFORMATION DISCOVERY, INFORMATION HARVESTING, KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY IN DATABASES (KDD), KNOWLEDGE EXTRACTION. See also GENETIC DATA MINING. NOTE: Methodological approaches to data mining include cluster analysis, linkage analysis, visualization, algorithms, categorization analysis. Technologies used in data mining include NEURAL NETWORKS, decision trees, time series analysis, GENETIC ALGORITHMS, hybrid approaches, FUZZY LOGIC and statistics. [10:2833]
DATA PATTERN PROCESSING - See DATA MINING
DATA REASONING - The primary symbolic process which combines related measurement and decision data to infer the classification or intent of individual targets or larger target aggregates. See also EXPERT SYSTEM, DATA ASSOCIATION, DATA COMBINATION, DATA FUSION. [5:2]
DATA WAREHOUSE - A sophisticated database which comprises a complete repository of historical data for an organization. Its design emphasizes data storage efficiency and data reliability, rather than speed of extraction or currency of data. [10:2766] Compare with OPERATIONAL DATA STORE. See also DATA MINING. NOTE: In a data warehouse, data are stored at the lowest level of detail possible so that they can be searched, collected and re-shaped for any purpose.
DATAGRAM - (1) A data packet traveling through the Internet. [10:2619] (2) A PACKET carrying enough header information to be routed from its source to its destination independent of other packets and without any need to set up an end-to-end connection. [10:2632]
DATUM - In antisubmarine warfare, a datum is the last known position of a submarine, or suspected submarine, after contact has been lost. See also FLAMING DATUM. [1]
DAZZLE - Temporary loss of vision or a temporary reduction in visual acuity. See also FLASH BLINDNESS. [1]
DAZZLING - A COVER technique to hide the real by confusing the observer. [10:49]
DEAD HAND - A Russian ICBM launch system that, in the event of a U.S. first strike that would decapitate the top leadership in Moscow, provides for an automatic retaliatory launch against the United States. It is code-named Perimetr. [10:2860]
DEAD MAN'S SWITCH - See SPECIAL WEAPONS EMERGENCY SEPARATION SYSTEM (SWESS).
DECEPTION - Those measures designed to mislead the enemy by manipulation, distortion, or falsification of evidence to induce him to react in a manner prejudicial to his interests. [1] See also ELECTRONIC DECEPTION. NOTE: A notion of DECEPTION is to "show the false".
DECEPTION MEANS - Methods, resources, and techniques that can be used to convey information to a foreign power. There are three categories of deception means: physical means; technical means; and administrative means. [1*]
DECEPTIVE HOLOGRAPHIC IMAGING - The projection of an array of holographic images about certain locations to deceive the adversary into misallocation of resources, attention, and/or effort around the present operation. [10:2751]
DECEPTIVE JAMMING - The transmission of signals similar to the victim's transmissions but false, causing the enemy to misinterpret or misuse the received signals. []
DECEPTIVE NOISE - [ACOUSTIC JAMMING term] The simulating of ship noise, torpedoes, or transient sounds to deceive a submarine. [10:41]
DECIBEL - One-tenth of a Bel (named after Alexander Graham Bell), the number of decibels denoting the ratio of the two amounts of power being ten times the logarithm to the base 10 of this ratio. [3] NOTE: the abbreviation dB is commonly used for the term decibel. With P1 and P2 designating two amounts of power and n the number of decibels denoting their ratio, n = 10 log10(P1/P2) decibel. From this relationship, it can be seen that a 3dB decrease is a 50% reduction in power, approximately. For additional discussion, click . [11.2].
DECISION TECHNOLOGY SYSTEM - An information system to support all phases of decision making from problem recognition, through problem formulation, analysis, solution, interpretation, and implementation. The system can include management information systems, decision support systems, expert systems, executive information systems, office automation systems, and idea processing systems. [10:118]
DECONFLICTION - (1) The process of optimizing frequency usage in a tactical environment. See FREQUENCY DECONFLICTION. [] (2) The minimization of fratricide through SITUATIONAL AWARENESS (SA) and effective use of weapons. (3) The control of shipping to prevent interference with military operations. []
DECONVOLUTION - Processing of signal parameters to exclude undesirable effects, such as ambient noise and own signals. []
DECOUPLING TILE - Foam tiles applied to ships' hulls adjacent to main and auxiliary engine spaces to decouple the sound path between machinery noise and the external environment. []
DECOY - An imitation in any sense of a person, object or phenomenon which is intended to deceive enemy surveillance devices or mislead enemy evaluation. See also CHAFF. [1]
DECOYING - A deception technique which diverts attention to offer misleading or multiple options to the enemy. [10:49] NOTE: Examples of DECOYING are the diversionary strike and use of devices to simulate ships or aircraft.
DECOY SHIP - A ship CAMOUFLAGED as a noncombatant ship with its armament and other fighting equipment hidden, and with special provisions for unmasking its weapons quickly. [10:2764] Also called Q-SHIP.
DEEP SIREN - A surface-towed batwing-shaped low frequency (less than 2KHz) sonar system which permits submerged submarines to maintain communications with a task force while remaining on station (i.e., the submarine need not leave station to come to periscope depth to communicate with the task force). [10:2850]
DEFENSE INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE (DII)- The worldwide shared or interconnected system of computers, communications, data, applications, security, people, training, and other support structures serving a nation's military's information needs.
DEFENSE SWITCHED NETWORK (DSN) - A component of the Defense Communications System that handles Department of Defense (DoD) voice, data, and video communications. Formerly, the AUTOMATIC VOICE NETWORK (AUTOVON). []
DEFERENCE TONES - A NONLETHAL WEAPON consisting of sophisticated arrays that can project a voice, or other sound, to a particular location so that the sound can only be heard at that particular location. [10:2754]
DEFERRED TIME - Operations yielding results than can be manifested, displayed, or printed lager. Contrast with REAL TIME. []
DEGAUSSING - The neutralization of the strength of the magnetic field, e.g., of a vessel. [3] See also DEPERMING.
DEINTERLEAVING - The process of separating simultaneously-received signals from multiple emitters so that the pulses of a single emitter can be isolated and identified. []
DELAYED-ACTION AGENT - A NONLETHAL WEAPON consisting of a nonlethal agent (e.g. CALMATIVE AGENT) that has a controlled delay time before becoming effective. [10:2751]
DELOUSING - The distinguishing of returning Blue (friendly) strike aircraft from tag-along Red (enemy) aircraft so as to (1) avoid firing upon friendly forces, (2) provide assistance in getting them home, and (3) recognize and counter any tag-along Red aircraft. []
DELTA JAMMING - A SELF-SCREENING ECM technique that causes angle errors in monopulse radars by transmitting two RF signals whose frequencies are separated in such a way as to cause false intermediate frequency (IF) signals in the victim radar's IF amplifier. [8]
DEMON DIALER - A relatively unsophisticated computer program that dials the same telephone number continually until it detects an answer. [] Compare with WARDIALER.
DENIAL - Preventing an adversary from gaining information on friently intentions, disposition or capabilties. []
DENIAL OF SERVICE (DOS) ATTACK - See E-MAIL BOMB.
DENSE WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXING (DWDM) - A LASER technique which enables a single strand of fiber to carry up to 400 gigabits per second. It features transmission of very closely spaced wavelengths by dividing the laser light among 80 different channels of varying colors. [10:2630]
DEPARTMENT/SERVICE MILITARY DECEPTION - MILITARY DECEPTION planned and executed by Military Services about military systems, doctrine, tactics, techniques, personnel or service operations, or other activities to result in foreign actions which increase or maintain the originator's capabilities relative to adversaries. Department/Service Military Deception is a category of Military Deception. [1] See also DECEPTION, ELECTRONIC DECEPTION, MILITARY DECEPTION.
DEPERMING - To remove, as far as practicable, the permanent magnetic characteristics of a ship's hull by powerful external demagnetizing coils. [3] See also DEGAUSSING.
DESTRUCTIVE ELECTRONIC WARFARE - Those EW actions that are planned to damage or destroy enemy personnel, equipment, or facilities. [7:CJCS MOP 6, APPENDIX B]
DETECTOR - With respect to electromagnetic energy, a detector is a device for the indication of the presence of electromagnetic fields. [3]
DETUNING SKIRT - An electrical attachment to tower structures (e.g., cellular telephone tower) used to prevent the tower from reflecting or reradiating AM signals, which would affect the intended directional characteristics of the AM station. [] NOTE: A detuning skirt consists of three or more wires spaced equally about the structure and strung alongside its length at a distance of 18-30 inches. The wires of the skirt are bonded to the tower at the top, and are connected to a wire hoop around its bottom (the 'skirt'). The wires are kept from touching the tower at any place (except the top) by insulators, if required. The hoop is connected to an electrical tuning circuit housed near the tower, which is tuned to the signal of interest. After proper tuning (or 'detuning') the tower presents a high impedance to the signal and, therefore, will not reflect nor reradiate it. [10:2897]
DEUTERIUM FLUORIDE (DF) LASER - The DF laser is chemically the same as as the HYDROGEN FLUORIDE (HF) LASER. However, the increased mass of heavy hydrogen deuterium, shifts the laser wavelengths to 3.5 Ám to 4 Ám. This range is superior to the HF laser range for transmission through the atmosphere. [10:2607] See also MID INFRARED CHEMICAL LASER (MIRACL).
DIBIT - A group of two BITs. [] See also BYTE. NOTE: The four possible states for a dibit code are 00, 01, 10, and 11.
DICKE FIX - An ECCM technique used to counter SWEEP JAMMING. []
DIFFERENCE ACOUSTIC WAVE GENERATION SYSTEM (DAWGS) - A NONLETHAL ACOUSTIC WEAPON consisting of electro-pneumatic acoustic generators which produce a high power acoustic beam with precise frequency control. [10:2731]
DIFFERENTIAL GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM (DGPS) - A system in which on-shore GPS stations measure the difference between their actual position and the GPS measurement, then broadcast a correction signal for navigators aboard nearby ships to use. Positions can be determined to within 3 meters. [10:2680]
DIFFUSE REFLECTION - Reflection from a rough surface. Contrast with SPECULAR REFLECTION. [3]
DIGITAL BATTLEFIELD - A combination of automated position location, communications, information, targeting, and sensor systems that provides a common operational picture. [10:2852]
DIGITAL DUST - See SMART DUST
DIGITAL MICRO-MIRROR DEVICE (DMD) - A space-and-cost-effective alternative to the CATHODE RAY TUBE (CRT). A DMD creates images using millions of tiny mirrors, each a PIXEL. The DMD projects light with a grid-like series of pixels and the light reflected from the pixels creates detailed pictures. Each micro-mirror element is suspended at two corners, enabling it to turn on microscopic torsion hinges. Computer-driven electrical impulses to a pad beneath the matrix of mirrors causes the pixels to tilt and direct light toward or away from an imaging lens and onto a viewing screen. Optical resolution is improved by increasing the number of mirrors used. DMDs may have from 440,000 to more than two million mirrors. [10:2523*]
DIGITAL MODULAR RADIO (DMR) -- A reprogrammable radio that permits the operator to instantly change the device's bandwidth, modulation and security waveforms with software commands. The digital modular radio can also function as a router, moving voice, data and video over a wide variety of wireline and wireless paths. Users can reprogram the radio through a Windows-like interface from a personal computer, or remotely over wireless and wireline, or over Internet pathways. [10:2661] Also called SOFTWARE REPROGRAMMABLE RADIO.
DIGITAL RADAR - A radar in which system control and signal processing are effected by digital computer systems. [10:2389] Contrast with ANALOG RADAR.
DIGITAL RADIO FREQUENCY MEMORY (DRFM) - An electronic device consisting of a random access memory, analog-to-digital converters, digital-to-analog converters, and associated circuitry which provides the ability to capture threat emissions and to generate precise replicas for transmission at a later time. [4:18]
DIGITAL SIGNATURE - A method for providing proof of the identity of the sender of a message and verification that the message has not been altered in transit. [10:2817]
DILUTION CHAFF - See DISTRACTION CHAFF.
DIODE - (1) A VACUUM TUBE containing two elements: CATHODE and ANODE (plate). [] (2) A semiconductor device having two terminals and exhibiting a non-linear voltage-current characteristic. [3*]
DIODE LASER (DL) - A LASER in which a semiconductor is used as the light-emitting source. The choice of semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the output light, with very little tunability permitted for a given semiconductor material. [10:2559] See also CRYSTAL LASER, DYE LASER, GAS LASER. NOTE: Unlike other lasers, DIODE LASERs have no energy storage states, but they can be made very small, yet powerful.
DIPLEXING - The use of a single antenna to transmit on two separate frequencies simultaneously. []
DIPOLE - (1) A metal radiating structure of one-half wave-length in length so that the current has a node at each end of the element [3*] (2) A strip of metal cut to one-half wavelength. [] Synonymous with HALF-WAVE ANTENNA.
DIRECT COUPLING - (1) The coupling or conduction of signals or noise from one conductor to another by means of direct hardwire contact ( as opposed to inductive or capacitance coupling ) or an optical fiber to fiber direct interface ( as opposed to, say, a lens interface ). [10:17*] (2)The injection of a virus directly into the target system. See also COMPUTER VIRUS COUNTERMEASURES. [10:47] NOTE: Direct coupling could be accomplished by a continuous transmission of the virus code at the same time that the victim is receiving a valid transmission.
DIRECT FINGER READER (DFR) - A BIOMETRIC DEVICE, placed on a peripheral (e.g., keyboard or mouse), which will allow usage of the peripheral only by users whose fingerprints are on file in the system's database of authorized users. [10:2874]
DIRECT JAMMING SUPPORT - A type of TARGET AREA JAMMING SUPPORT in which the jamming aircraft flies directly through hostile territory, sometimes with the strike package it will support. [10:2521] See also AREA JAMMING SUPPORT, CLOSE-IN JAMMING SUPPORT, CORRIDOR JAMMING SUPPORT, STAND-OFF JAMMING SUPPORT.
DIRECT SEQUENCE SPREADING - A SPREAD SPECTRUM technique which employs a code-carrier to multiply a signal containing the information to be transmitted. Direct Sequence Spreading uses the entire spread bandwidth as an instantaneous bandwidth. Contrast with FREQUENCY HOPPING, TIME HOPPING. [4:13]
DIRECT (FREQUENCY) SYNTHESIS (DS) - FREQUENCY SYNTHESIS where generation of desired frequencies is achieved by using a stable oscillator to generate a single reference frequency. [10:2616] Contrast with INDIRECT SYNTHESIS (IS).
DIRECT VIEW OPTICS (DVO) - A generic term for any set of optics designed to enhance the human eye, which is the sensor in such a system. [] NOTE: An example of DVO is a pair of binoculars.
DIRECTED ENERGY (DE) - An umbrella term covering technologies that relate to the production of a beam of concentrated electromagnetic energy or atomic or subatomic particles. [7:CJCS MOP 6, APPENDIX B]
DIRECTED ENERGY DEVICE - A system using DIRECTED ENERGY primarily for a purpose other than as a weapon. Directed energy devices may produce effects that could allow the device to be used as a weapon against certain threats, for example, laser rangefinders and designators used against sensors that are sensitive to light. [7:CJCS MOP 6, APPENDIX B]
DIRECTED ENERGY WARFARE (DEW) - Military action involving the use of DE weapons, devices, and countermeasures to either cause direct damage or destruction of enemy equipment, facilities, and personnel, or to prevent hostile use of the electromagnetic spectrum through damage, destruction, and disruption. It also includes actions taken to protect friendly equipment, facilities, and personnel and retain friendly use of the electromagnetic spectrum. [7:CJCS MOP 6, APPENDIX B]
DIRECTED ENERGY WEAPON (DEW) - (1) A system using directed energy primarily as a direct means to damage or destroy enemy equipment, facilities, and personnel. [1] (2) A HARD-KILL ECM weapon employing directed energy, such as PARTICLE BEAM, HIGH ENERGY LASER, LASER ZAPPER, high powered microwaves, etc. []
DIRECT EW SUPPORT - Mission support in which EW platforms accompany protected units, e.g., strike aircraft. See also ACCOMPANYING JAMMING. Contrast with STAND-IN EW SUPPORT, STAND-OFF EW SUPPORT. [10:127*]
DIRECTIONAL INFRARED COUNTERMEASURES (DIRCM) - The use of high-powered directional infrared jamming. [10:98] See also INFRARED COUNTERMEASURES. NOTE: A DIRCM engagement consists of four phases: (1) Detect - in which the missile warning system (MWS) detects a missile plume and sends a signal to the processor; (2) Handoff - in which the processor sends threat information to the DIRCM transmitter; (3) Track - in which the transmitter slews to the location of the threat and the flexible turret system (FTS) acquires the signal, locks on to the threat and tracks the target; and (4) Jam - wherein the transmitter sends a modulated beam of infrared (IR) energy to the missile seeker and jams its guidance signal. [10:2841]
DIRECTION FINDING (DF) - See RADIO DIRECTION FINDING.
DIRECTIVITY - (1) The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions. [3] (2) The ratio of the power scattered back in the radar's direction to the power that would have been BACKSCATTERED had the scattering been uniform in all directions. []
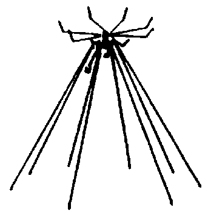
DISCONE - A biconical antenna ( two conical conductors that have a common axis and vertex and are excited (or connected to the receiver) at the vertex ) for which one of the cones has a vertex angle of 180 degrees. [3] NOTE: Discone antennas have wide BANDWIDTH characeristics and are omni-directional.
| Discone Antennas | |
 |
 |
DISK OPERATING SYSTEM (DOS) - A popular macrocomputer operating system. []
DISORIENTATION DEVICE - NONLETHAL WEAPON ammunition which, upon impact, inflicts an electric shock that potentially causes disorientation of the target individual. [10:2745]
DISSIMILAR SOURCE INTEGRATION - The integration of information or data from diverse sources, e.g., RADAR, IDENTIFICATION, FRIEND OR FOE (IFF), ELECTRONIC WARFARE (EW), acoustic, visual, etc.... []
DISTRACTION - The successful lock-on-before-launch (LOBL) of weapons to be launched at false targets or decoys, or lock-on-after-launch (LOAL) of weapons to initially acquire and home on false targets or decoy. See also SEDUCTION. [10:126]
DISTRACTION CHAFF - CHAFF which presents a credible decoy to a missile before it acquires track on the target ship or after it has been subjected to angle or range gate stealing. [4:16] Synonymous with DILUTION CHAFF. Contrast with SEDUCTION CHAFF. See also LOCK-ON METHOD OF CHAFF DEPLOYMENT and DUMP METHOD OF CHAFF DEPLOYMENT. NOTE: Distraction chaff need not have as great a RADAR CROSS SECTION as the target ship, but should be deployed at some distance away to effectively "distract" the missile.
DISTRIBUTED COMMON GROUND SYSTEM (DCGS) - A system which allows remote exploitation of multiple sensors by groundstations in the continental United States (CONUS). [10:2865]
DISTRIBUTED INTERACTIVE SIMULATION (DIS) - A protocol for DISTRIBUTED VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTs developed by the U.S. military so that COMPUTER GENERATED FORCEs and manned simulators might interact on a large scale; now an IEEE standard. [10:2595]
DISTRIBUTED POWER (DP) - Modular electric generation or storage located near its point of use. [10:2885] NOTE: In addition to providing stand-alone power for isolated sites, distributed power ensures electricity during system outages and allows customers to save money by switching to distributed generation during high-cost peak periods. [10:2885]
DISTRIBUTED SENSING - See MULTISENSOR DATA FUSION
DISTRIBUTED VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT (DVE) - A VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT in which several users may interact and whose elements exist on two or more platforms. [10:2595]
DISTRIBUTIVE EXPLOSIVE TECHNOLOGY (DET) - A surf mine-clearing system consisting of a dual-rocket-deployed system that fires an explosive array (or net) charge from a Landing Craft, Air Cushion (LCAC) to destroy mines in the shallow-water zone from three feet up to the beach. [10:2790] Compare with SHALLOW-WATER ASSAULT BREACHING (SABRE) SYSTEM. See also AIRBORNE MINE-NEUTRALIZATION SYSTEM (AMNS), RAPID AIRBORNE MINE-CLEARANCE SYSTEM (RAMICS), and SHALLOW WATER INFLUENCE MINE SWEEP (SWIMS) SYSTEM.
DNA CRYPTOGRAPHY - A cryptographic technique in which each letter of the alphabet is converted into a different combination of the four bases that make up the human deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). A piece of DNA spelling out the message to be encrypted is then synthesized, and the strand is slipped into a normal fragment of human DNA of similar length. The end result is dried out on paper and cut into small dots. As only one DNA strand in about 30 billion will contain the message, the detection of even the existence of the encrypted message is most unlikely. [10:2815]
DOMAIN - A set of interconnected networks, GATEWAYs, and hosts. [10:2619]
DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) - The DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) is used on the Internet and other UNIX-based networks to map computer names to Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. []
DONGLE - A small security device that attaches to a computer port to control access to a specific software application. [10:2855] NOTE: A dongle-protected program will run only when its dongle is attached to the computer.
DOPPLER EFFECT - The effective change of frequency of a received signal due to the relative velocity of a transmitter with respect to a receiver. [3]
DOPPLER RADAR - A radar which utilizes the Doppler effect to determine the radial component of relative radar target velocity or to select targets having particular radial velocities. [3]
DOPPLER RESOLUTION -- The minimum difference in Doppler that permits target resolution among multiple contacts. []
DOPPLER SHIFT - The magnitude of the change in the observed frequency of a WAVE due to the DOPPLER EFFECT. The unit is the HERTZ. [3] For additional discussion, click . [11.2]
DOUBLE-DIAPHRAGM RADOME - A RADOME possessing a second diaphragm, perforated with holes about 3.8mm in diameter, positioned outside the conventional diaphragm-type radome, forming a plenum with the inner diaphragm. Air forced into the plenum flows out through the holes, floating raindrops away from the outer surface. Also called RAIN-BLOWING PLENUM [10:99] NOTE: A double-diaphragm radome drives raindrops away from the antenna feed horn. It thus nearly eliminates the increase in noise temperature that occurs when water covers a radome. This design is particularly useful for X-band and higher frequencies, which are especially susceptible to the effects of water.
DOUBLE PULL -- An ECM technique involving coordinated us of VELOCITY GATE PULL OFF (VGPO) and RANGE GATE PULL OFF (RGPO). []
DOUBLE PULSING - An ECCM technique used by tracking radars against SELF-SCREENING ECM pulse repeaters by exploiting the ECM equipment's dead time which occurs after an ECM pulse transmission. [8]
DOUBLER - With respect to LASERs, certain non-linear crystals which oscillate at the frequency of the input laser and also at a at a harmonic of twice that of the input laser's frequency. For example, with the input of a 10.6 micron laser light (FAR INFRARED), the output of a doubler will also include a 5.3 micron (MID INFRARED) [10:2559] See also OPTICAL PARAMETRIC OSCILLATOR, TRIPLER.
DOUBLY-CONFORMAL ANTENNA - A CONFORMAL ANTENNA which does not protrude from the vehicle surface nor intrude into the vehicle support structure. [10:54] See also MICROSTRIP ANTENNA, CONFORMAL ANTENNA ARRAY, SHARED-APERTURE ANTENNA.
DRIFT SPACE - In a VACUUM TUBE, A region substantially free of externally applied alternating fields, in which a relative repositioning of the electrons takes place. [3] See also KLYSTRON.
DRIVER'S VISION ENHANCER (DVE) - A device which provides the driver of a vehicle with the ability to drive at night and under obscured conditions. []
DRONE - (1) A land, sea, or air vehicle that is remotely or automatically controlled. [1] (2) A pilotless air vehicle pre-programmed prior to launch to accomplish a set of functions with no further human intervention. The drone may use on-board sensors to autonomously make mission adjustments. [10:25] See also REMOTELY PILOTED VEHICLE, UNMANNED AIR VEHICLE.
DRY-ICE WEAPON - A NONLETHAL WEAPON consisting of a dry-ice bomb that incapacitates subjects by overwhelming them with CO2 at concentrations above 15% by volume. [10:2745] NOTE: Because high concentrations of CO2 can be lethal, oxygen must be available to treat the affected individuals as soon as possible.
DUAL ANAMORPHIC REFLECTOR TELESCOPE (DART) - A low-mass membrane telescope for use in earth-orbiting and deep space applications. DART uses a thin membrane for the reflective surfaces, which allows for greater aperture size without increasing the telescope's overall mass. DART consists of two parabolic-cylindrical trough-shaped reflectors aligned with each other to produce a point focus. The mirrors are formed by tensioning a reflective foil over a frame with a parabolic contour along one axis. [10:2886] NOTE: As the aperture of a DART device increases, the mass ratio of structure to reflector decreases - the opposite of traditional telescopes. [10:2886]
DUAL-MODE EXPENDABLE - See FLAMING RECEIVER.
DUAL TONE MULTI FREQUENCY (DTMF) - Also known as Touch Tone™, DTMf, or dual tone multi frequency, uses two tones to represent each key on the telephone touch pad. (The A, B, C, and D keys were used for the U.S. military's Autovon phone system).
sampled at 8Khz
When any key is pressed, the tone of the column and the tone of the row are generated, hence dual tone. As an example, pressing the '5' button generates the tones 770Hz and 1336Hz. [10:2717] For additional details, click .
DUAL-USE TECHNOLOGY - Technology which is usable in both military and civilian applications. []
DUAL WARNING PHENOMENOLOGY - Deriving warning information from two systems observing separate physical phenomena (e.g., radar/infrared or visible light/X-ray) associated with the same events to attain high credibility while being less susceptible to false reports or SPOOFING. [1]
DUCTING - A phenomenon in which radio waves are bent to conform to the curvature of the Earth (e.g., in the troposphere), rather than traveling in a straight line, thus extending the range of propagation. [] NOTE: Ducting of sound waves can occur within temperature inversion layers in water, as well.
DUMB AMMUNITION - A generic classification. Dumb ammunition follows a purely ballistic trajectory with spin stabilization. There is no guidance, and errors in delivery are due primarily to pointing, propellant burn, and meteorological factors. [10:19] Contrast with BRILLIANT AMMUNITION, SMART AMMUNITION. NOTE: An example of dumb ammunition is the CLUSTER BOMB UNIT.
DUMB MINE - A mine which has no self-destruct capability, and therefore remains a threat while implanted. [] Contrast with SMART MINE.
DUMMY LOAD - A dissipative but essentially non-radiating substitute device having impedance characteristics simulating those of the substituted device. [3]
DUMP METHOD OF CHAFF DEPLOYMENT - An EW technique whereby the seeker of an inbound missile is first seduced by a jammer using angle or range-gate stealing and forced to lock on to the already deployed DISTRACTION CHAFF decoy. [4:21] Contrast with LOCK-ON METHOD OF CHAFF DEPLOYMENT.
DUTY CYCLE - See DUTY FACTOR.
DUTY FACTOR - With respect to radar, the ratio of the active, or "ON," time within a specified period to the duration of the specified period. [3] Note: This is sometimes called DUTY CYCLE. Click HERE for a discussion of duty cycle [11.2].
DWELL TIME - (1) A measure of the signal-handling rate of a receiver. Specifically, dwell time is the difference in acceptance time of two signals spaced in frequency. [10:2] (2) In ECCM, DWELL TIME is the length of time that a sensor looks at an emitter. [] NOTE: A receiver is not always ready to accept a new signal because it may be "dwelling" on a different signal at that instant.
DWELL WALK PROGRAMMING - An ECM technique to deceive the tracking gate of a victim radar. The ECM receiver first captures the angle-gate, range-gate, or velocity-gate of the victim radar and repeats the parameters for a short time (dwell) so that the victim radar locks on to the ECM signal. Slowly - to maintain inside the tracking limits of the victim radar - the ECM set varies (walks) the angle, range, or velocity of the jamming signal to simulate a movement away from the actual ECM platform's position. After walking ten or more times the width of the victim radar's tracking gate, the ECM set stops radiating, leaving the victim radar with no target, thus breaking the lock-on. This process is repeatable, and can be used in conjunction with other complementary ECM techniques. [8]
DYE LASER - A LASER in which the emitting element is a liquid. [10:2559] See also CRYSTAL LASER, DIODE LASER, GAS LASER. NOTE: Dyes can be toxic and combustible and have a relatively short operating life.
DYNAMIC HYPERTEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE (DHTML) -- An extension of HYPERTEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE, providing more control over the appearance and position of elements on a Web page. DHTML is considered 'dynamic' because it provides a way to include elements on a Web page that download to a user's Web browser along with the page but do not become visible until the user interacts with them. This means that when the user interacts with the elements, they activate without requiring any action from the Web site's server. []
DYNAMIC MEMORY ACCESS (DMA) - Direct data transfer between memory and peripherals, without going through the CPU. []
DYNAMIC RANGE - The difference, in decibels, between the overload level and the minimum acceptable signal level in a system or transducer. [3]
October 13, 2001 05:16 PM -0400