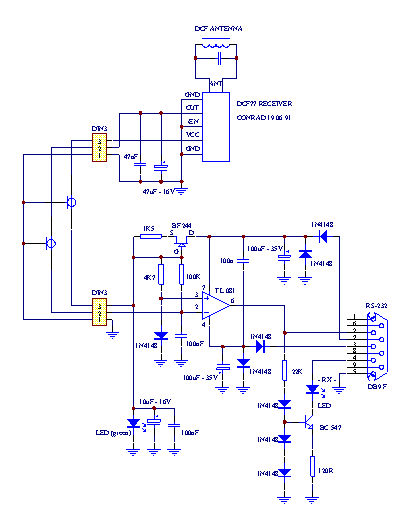


The circuit interfaces a commercial DCF77 receiver (available for about $15)
with a PC using the RS232 serial port. By rewriting the program it's possible to
interface also different systems or different I/O ports.
The power is driven from three lines of the RS232 port (that is full
protected against short circuits). The DTR and RTS lines are
set high (+12V on the port) and the TXD is kept low
(-12V) for the supply of the receiver.
The RTS line gives positive power to the circuit and the
DTR powers only the monitor LED that is kept separated from the
rest of the circuit because of its high current peaks.
All the diodes 1N4148 connected to the port and to the BC.547B
transistor protect the circuit when the port is wrong programmed or
not initialized.
The JFET BF.244, the 1.5kOhm resistance and the second
LED compose a precise voltage reference of about 1.8V needed for
supplying the receiver. This LED is traversed by a low current and it's
not particularly bright.
The TL.081 is used as comparator and line driver; its
reference voltage is set at 0.6V on its non-inverting input by a 1N4148
diode.
The TL.081 returns the DCF77 signal (RS232 compatible) on the
RXD pin. This pin must always be high (-12V since pin is inverted)
and go low one per second (when a bit is received).
Some receivers have an inverted output, and to use them just swap
pins 2 and 3 of the TL.081.
The receiver should stay away from the PC and from the comparator circuit
because pulse noise inhibits normal reception.
The DCF77 standard impose a pulse time of 200ms for set bits and a pulse
time of 100ms for clear bits, but, since receivers usually use about
40ms for a safe reception these times are reduced to 160 and
60ms. When receiving this pulses with the PC UART 8250 (or
better) at the speed of about 40 baud N81 a 160ms pulse will produce
a $80 or a $C0 byte and a 60ms a $FE or $FC.
This is a picture of the interface: the lower connector is the RS232 cable and the other one comes from the antenna.


| Back to DCF77. | 
| Back to the home page. |

| Previous page. | 
| Next page. |


| Questa pagina è disponibile anche in italiano. |
