Buy and download my eBook: The
PID Control Algorithm:
How It Works and How To Tune It. 58pp
MS Word 97 or .pdf file
only $9.50.
Get more details, buy, and download
| ControlSim The PID controller and process simulator based on MS Excel spread sheets. $45.00 | Click here to get more details, buy, and download |
Buy and download my eBook: The
PID Control Algorithm: |
Get more details, buy, and download |
Chapter 2
The Process Response to the Controller
Steady state relationships:
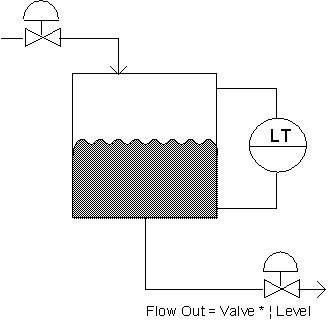
Relating valve change to measurement change
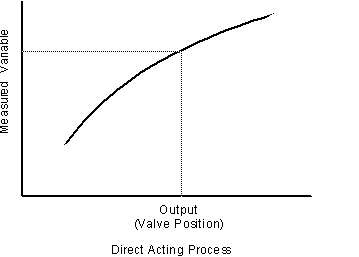
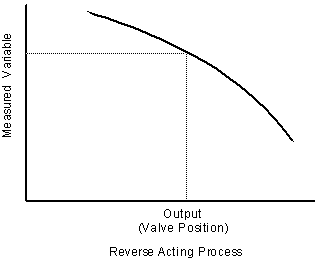
Steady state relationships:
changing load
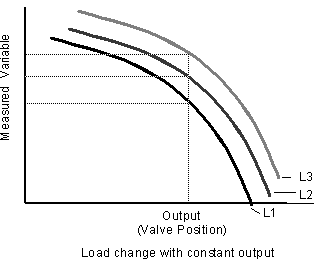
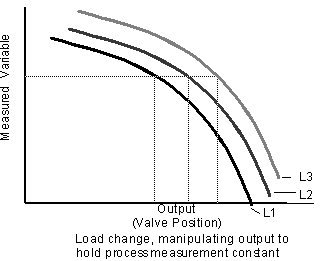
When the load changes, either the process value changes or the valve position must be changed to compensate for the load change.
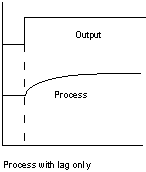
Process Dynamics: Simple lag
Process Dynamics: Dead time
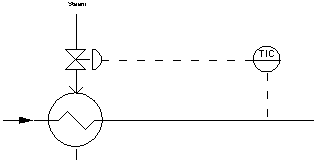
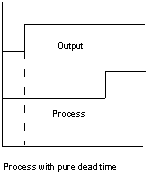
Dead Time: A delay in the loop due to the time it takes material to flow from one point to another
Also called: Distance Velocity Lag
Transportation Lag
 |
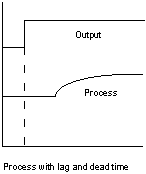 |
Most loop combine dead time and lag.
Measurement of dynamics
The dynamics differ from one loop to another.
However, they usually result in a response curve like this:
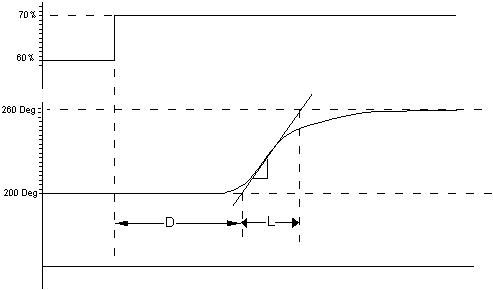
L is Lag—the largest lag in the process loop.
D is "Pseudo Deadtime"—the sum of the deadtime and all lags other than the largest lag.
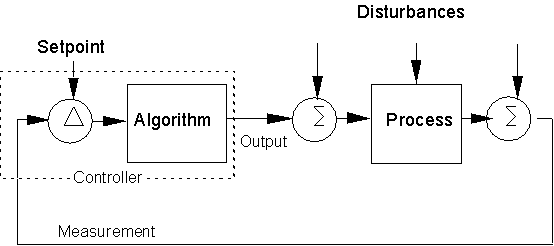
Disturbances
Almost all processes contain disturbances.
Disturbances can enter anywhere in the process.
The effect of the disturbance can depend on where it enters the loop.
Most disturbances cannot be measured.
go to chapter 3: the PID algorithm