2-Layer Motors
wwwwwwwwwwwwwww
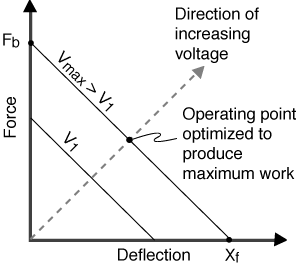
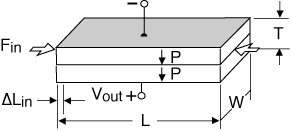
Two -layer elements can be made to elongate, bend, or twist depending on the polarization and wiring configuration of the layers. A center shim laminated between the two piezo layers adds mechanical strength and stiffness, but reduces motion.
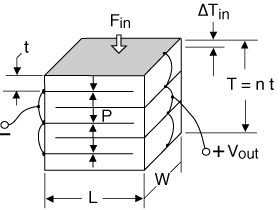
"2-layer" refers to the number of piezo layers. The "2-layer" element actually has nine layers, consisting of: four electrode layers, two piezoceramic layers, two adhesive layers, and a center shim. The two layers offer the opportunity to reduce drive voltage by half when configured for parallel operation.
Extension Motors:
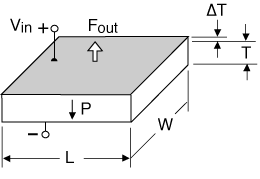
A 2-layer element behaves like a single layer when both layers expand (or contract) together. If an electric field is applied which makes the element thinner, extension along the length and width results. Typically, only motion along one axis is utilized. Extender motion on the order of microns to tens of microns, and force from tens to hundreds of Newtons is typical.
Bending Motors:
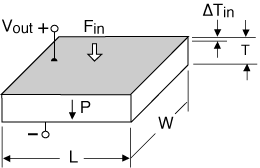
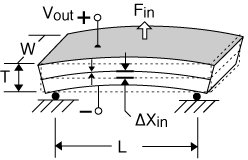
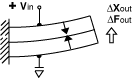
A 2-layer element produces curvature when one layer expands while the other layer contracts. These transducers are often referred to as benders, bimorphs, or flexural elements. Bender motion on the order of hundreds to thousands of microns, and bender force from tens to hundreds of grams, is typical.
These illustrations show several common bending configurations. The variety of mounting and motion options make benders a popular choice of design engineers. |

2-Layer Transverse Motor, expanding lengthwise
For extension motors of the same thickness:
Xf, Free Deflection  L
L
Fb, Blocked Force  W
W
Fr, Resonant Frequency  I/L
I/L
C, Capacitance  L x W
L x W |
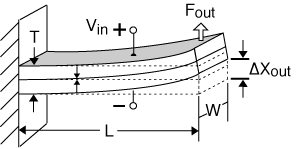
Bending Motor, cantilever mount
For cantilevered benders of the same thickness:
Xf, Free Deflection  L2
L2
Fb, Blocked Force  W/L
W/L
Fr, Resonant Frequency  I/L2
I/L2
C, Capacitance  L x W
L x W
Characteristics: End takes on an angle. Simple to mount. |
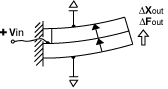
Bending Motor, simple beam mount
To convert cantilever to simple beam performance:
Xf = 1/4 X cantilever motion
Fb = 4X cantilever force
Fr = 3X cantilever frequency
C = same as cantilever capacitance
Characteristics: center moves up and down in a parallel plane. |
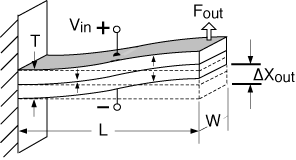
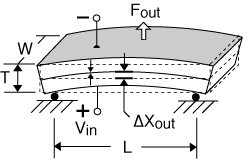
Bending Motor, "S" configuration, cantilever mount
To convert cantilever to "S" beam performance:
Xf = 1/2 x cantilever motion
Fb = 1/2 x cantilever force
Fr = same as cantilever frequency
C = same as cantilever capacitance
Characteristics: end moves up and down in a parallel plane |
|