| Reflectometer
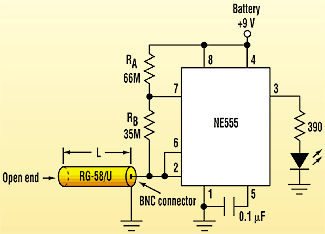
Here's a neat little circuit from Electronic Design Magazine..... Inexpensive "Reflectometer" Locates An Open Circuit Along A Cable by Arthur E. Edang Faults such as opens, shorts, or mismatches can be precisely located along the length of a cable by using a time-domain reflectometer. This device launches a rectangular pulse toward the cable's end and waits for an echo signal. The time between the start of the pulse and the arrival of the echo is then converted in terms of distance, allowing the fault to be accurately located. An oscilloscope is typically used to obtain the elapsed time reading. To detect ordinary open circuits along the cable, however, a simple, low-cost 555 timer IC operating in astable mode can be employed. Coaxial cables have distributed capacitances per unit length, which may be used to replace an actual capacitor (see the figure).
A simple and inexpensive "reflectometer" locates cable breaks using the distributed cable capacitance and ratiometric calculations. The LED will blink at a rate inversely related to the length of the cable, or at a frequency = 1.443/[(RA + 2RB)C]. For a 45-meter RG-58/U cable, the LED will flash at f1 = 1.67 Hz. When an open circuit is introduced at L2 = 25 meters from the IC, the LED will blink at about f2 = 3 Hz. By observing the increase in the LED's flash rate, the location (L2) of the open-circuit can be determined using the formula L2/L1 = f1/f2, where L1 = 45 meters. For other lengths of cable, the value of RA and RB
may need to be modified to find the values that make visual
checking possible. Alternatively, the output of the 555 can be
sent to a frequency counter for a more precise reading. |