
Believe it or not, the Earth behaves like an enormous electric circuit. The atmosphere is actually a weak conductor and if there were no sources of charge, its existing electric charge would diffuse away in about 10 minutes. There is a 'cavity 'defined by the surface of the Earth and the inner edge of the ionosphere 55 kilometers up. At any moment, the total charge residing in this cavity is 500,000 Coulombs. There is a vertical current flow between the ground and the ionosphere of 1 - 3 x 10^-12 Amperes per square meter. The resistance of the atmosphere is 200 Ohms. The voltage potential is 200,000 Volts. There are about 1000 lightning storms at any given moment worldwide. Each produces 0.5 to 1 Ampere and these collectively account for the measured current flow in the Earth's 'electromagnetic' cavity.
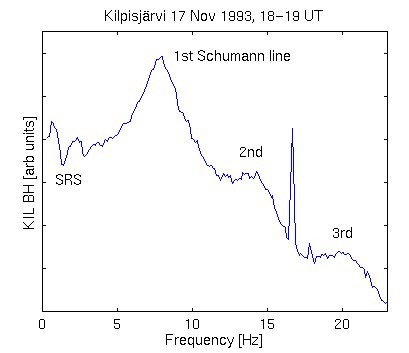
The Schumann Resonances are quasi standing wave electromagnetic waves that exist in this cavity. Like waves on a spring, they are not present all the time, but have to be 'excited' to be observed. They are not caused by anything internal to the Earth, its crust or its core. They seem to be related to electrical activity in the atmosphere, particularly during times of intense lightning activity. They occur at several frequencies between 6 and 50 cycles per second; specifically 7.8, 14, 20, 26, 33, 39 and 45 Hertz, with a daily variation of about +/- 0.5 Hertz. So long as the properties of Earth's electromagnetic cavity remains about the same, these frequencies remain the same. Presumably there is some change due to the solar sunspot cycle as the Earth's ionosphere changes in response to the 11-year cycle of solar activity. Schumann resonances are most easily seen between 2000 and 2200 UT.
Given that the earth's atmosphere carries a charge, a current and a voltage, it is not surprising to find such electromagnetic waves. The resonant properties of this terrestrial cavity were first predicted by the German physicist W. O. Schumann between 1952 and 1957, and first detected by Schumann and Konig in 1954. The first spectral representation of this phenomenon was prepared by Balser and Wagner in 1960. Much of the research in the last 20 years has been conducted by the Department of the Navy who investigate Extremely Low Frequency communication with submarines.
For more information, see:
"Handbook of Atmospheric Electrodynamics, vol. I", by Hans Volland, 1995 published by the CRC Press. Chapter 11 is entirely on Schumann Resonances and is written by Davis Campbell at the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, Fairbanks AK, 99775. There is also a history of this research and an extensive bibliography. You can also visit the University of Oulu web page.