Buy and download my eBook: The
PID Control Algorithm:
How It Works and How To Tune It. 58pp
MS Word 97 or .pdf file
only $9.50.
Get more details, buy, and download
| ControlSim The PID controller and process simulator based on MS Excel spread sheets. $45.00 | Click here to get more details, buy, and download |
Buy and download my eBook: The
PID Control Algorithm: |
Get more details, buy, and download |
Chapter 4
Additional PID Concepts
Interactive or Noninteractive algorithm
"Interactive" and "Noninteractive" refer to interaction between the reset and derivative terms. This is also known as "series" or "parallel" derivative.
Almost all analog controllers are interactive.
Many digital controllers are non-interactive, some are interactive
The only difference is in the tuning of controllers with derivative.
Non-Interactive (Parallel):
Out = G
(e + R+ D ) Interactive (series):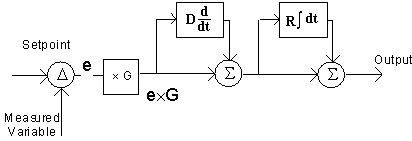
Out = (RD+1)G
(e + R+D )Converting between interactive and non-interactive
Applies only to 3-mode controllers
To convert from non-interactive to interactive:
Gn = Gi (1 + Ri Di)
Rn = Ri/(1 + Ri Di)
Dn = Di/(1 + Ri Di)
• In other words, with a non-interactive controller the gain should be higher, the reset rate lower, and the derivative lower than on a commercial interactive controller.
External feedback
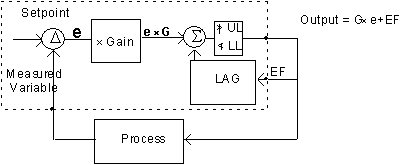
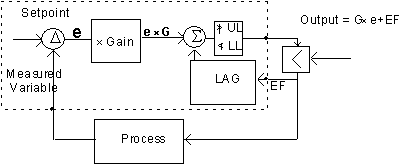
Saturation Properties
Another difference is in the "Saturation Properties"
eg. what happens when output has been at the upper or lower limit.
Standard algorithm
Described on previous page.
Output stays at limit until measurement crosses setpoint.
"Integrated velocity form"
Similar to equation:
Output = Last output + gain
x (error - last error + reset x error)Output pulls away from limit one reset time before measurement crosses setpoint.
• For most applications, there is no difference. For some batch startup problems, the "integrated velocity form" algorithm works best.
• Standard works best for high gain/low reset rate applications.
| Buy and download my 21 page e-book on the PID algorithm. MS Word 97 format only $5.00 |
 |
| Buy and download my 25 page e-book on the PID Tuning. MS Word 97 format only $6.00 |
 |