1. Introduction
2. Circuit Description
3. Construction
4. Calibration and Use
5. Alternative Construction
Introduction
A clip-on RF ammeter is not only useful for antenna experimenters but also as an aid to achieving good EMC in an amateur station. If some of the RF current from a transmitter flows into mains wiring, this can increase the chance of breakthrough problems in nearby TV, video or audio equipment etc. A clip-on RF ammeter allows this current to be measured, so that steps can be taken to minimise it.
For EMC investigations, you can also clip this meter on to coaxial cables, rotator cables and other wiring in your shack, to find out where the RF currents are flowing, and how big they are. You can also use this tool for measuring currents in wires and radials.
Instead of splitting a ferrite ring in half, RSGB EMC Committee member Dave Lauder, G0SNO. has been experimenting with various types of ferrite core which are already split. The best type he has found is a Maplin Computer Data Line Filter, 15mm [5/8-inch] hole diameter as shown in Fig 1 (below).
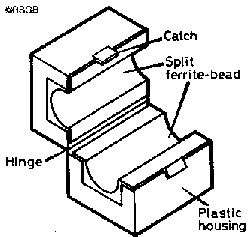
This is a large split ferrite bead with a 13mm diameter hole and a hinged plastic carrier which can be clipped around a cable. Although intended to be clipped on and left, with care it can be opened and closed repeatedly. It is intended for suppression of computer interference but can also be used as a wide-band current transformer. This type of split bead offers better coupling than a ring core and is usable from below 500kHz to over 50MHz.
What's needed for reasonable coupling is a split bead where the length of the hole is about 2.5 times the inside diameter. Make sure that the length of the hole is at least 30mm/1.25 inch for best results. Because most types of clip-on ferrite core are designed for EMI suppression, the grade of ferrite is generally OK for use as an RF transformer on the HF bands.
There are many sources for these cores. Preferably you need one that introduces very little series impedance at HF - you can check this using an Autek RF-1 or an MFJ-259. A core that has a substantial self-impedance at HF may affect the currents that you're trying to measure.
| Maplin Electronics (UK) +44/0 1702 554 000 Part No. BZ34M |
Fair-Rite Products Corp (USA) Part No. 0443164151 | |
| Farnell Components (UK) +44/0 113 263 6311 Stock No. 535-904 |
Radio Shack (USA) #273-105 | |
| RS Components / Electromail +44/0 1536 201 201 Stock No 222-4422 (but hole length is shorter than desirable) |
TDK Type ZCAT3035-1330 |
2. Circuit Description
3. Construction
4. Calibration and Use
5. Alternative Construction
Circuit Description
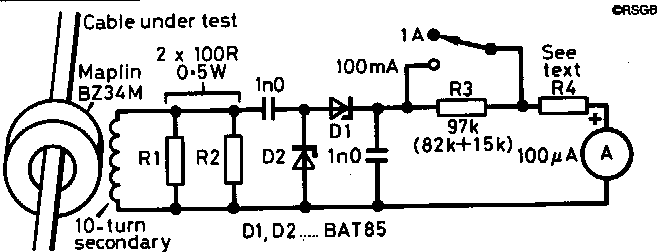
In the circuit in Fig 2 (above), a 10-turn secondary is wound on one half of the core and terminated by a 50-ohm load formed by R1 and R2 in parallel. When the core is clipped onto a cable, the cable under test forms the single turn primary winding of a transformer and in theory, 10% of the RF primary current flows in the secondary and through the 50-ohm load. (Note that more turns on the secondary would give less secondary current.) For primary currents up to 1A the power rating of the 50-ohm secondary load should be 1W. In practice, with the Maplin core, the current ratio is less than 10%, being fairly constant at 8% up to 30MHz and falling to 7.5% at 50MHz. At 14MHz for example, 1A RMS in the cable under test causes 80mA RMS to flow through the 50-ohm load which drops 4V RMS across 50 ohms.
Clipping the current transformer onto a cable adds a small series impedance which in theory is 0.5 ohms (secondary load divided by turns ratio squared) but in practice is about 2 ohms at 14MHz and 4 ohms at 28MHz. The voltage across R1/R2 is rectified by a voltage doubler rectifier using two BAT85 Schottky diodes. This gives a DC output about 2.8 times the RMS AC input voltage less the forward drop of the diodes. With a 100 microamp moving coil meter, the total resistance of (R3 + R4 + meter) should be 104 kohms on the 1A range. On the 100mA range, R3 is short-circuited and the resistance of (R4 + meter) should equal 6.8 kohms. On the 100mA range, the forward voltage drop of the diodes is significant, so that the minimum current which can be measured is 30mA and an extra scale should be marked on the meter as in Fig 3 (below). The response of the detector circuit on its own should be fairly flat up to 30MHz but it may be less accurate at 50MHz depending on lead inductance, layout etc. [For EMC work, tracing unwanted stray currents, you can see useful indications all the way up to 432MHz - G3SEK.]

2. Circuit Description
3. Construction
4. Calibration and Use
5. Alternative Construction
Construction
See below for photographs of G3SEK's alternative construction.
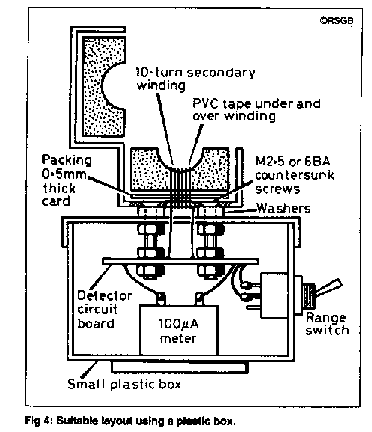
The meter can be mounted in a small plastic box with the current transformer mounted on the lid as shown in Fig 4.
The clip-on ferrite choke has two fixing holes in its plastic carrier. Carefully push out the half of the ferrite core then put two M2.5 or 6BA [1/8-inch] countersunk screws through the holes from the inside. Put a 0.5mm thickness of card (2 thicknesses of QSL card!) under the ferrite core before clipping it back into the carrier.
Now put a piece of PVC insulating tape onto the ferrite to protect the enamel insulation on the wire and wind 10 turns of enameled wire, about 26-28SWG (24-26AWG or 0.4mm) tightly round the ferrite core half. This will pull it down into the carrier which is why the card is needed Check that when the core is clipped shut, there is no gap between the halves, and that the plastic spring lugs on the top half are being pushed outwards by the core.
Cover the winding with epoxy or a piece of PVC tape to give it some protection in use.
2. Circuit Description
3. Construction
4. Calibration and Use
5. Alternative Construction
Calibration and Use
If required, the accuracy of the clip-on ammeter can be checked against a power meter on various bands, using the test set-up shown in Fig 5 (below).
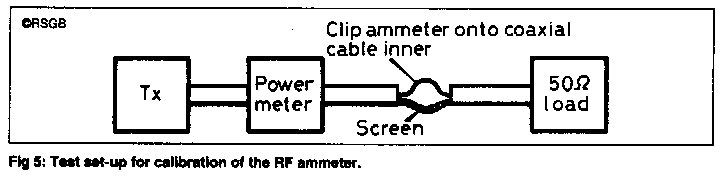
Clip the ferrite core around the coax inner only, with 50W into the load. The ammeter should show 1.0A. With 0.5W into the load, the ammeter should indicate 100mA. The split coax arrangement is only used for testing the meter in normal use, the meter should of course be clipped around the outside of the braid of unbroken coaxial cable. In this way, it does not respond to the current on the inner but only shows any current on the outside of the braid, which should ideally be zero. In practice, any current on the outside of the coax braid will form standing waves, causing the reading to vary as the ammeter is moved along the cable. It can also be clipped around a mains cable, particularly a transmitter mains cable to detect any RF current being injected into the mains wiring.
2. Circuit Description
3. Construction
4. Calibration and Use
5. Alternative Construction
Alternative Construction
G3SEK:
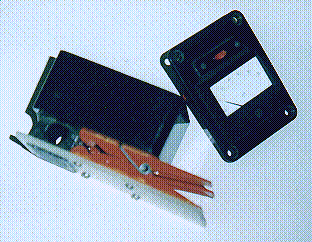
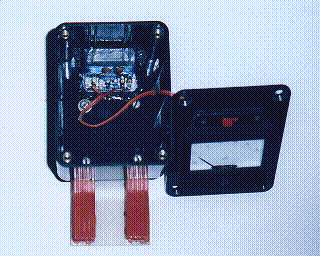
I found the original clip-on cores too fragile (Fig 1) - the plastic parts broke after being used a few times. As an alternative, I tried a "heavy duty" version of the earlier designs using a spring clothes-peg. The photos below show one version using two clothes-pegs in parallel.
The moving part of the ferrite core is glued into a hole in a piece of 1/8in (3mm) fibreglass sheet, which is itself glued and screwed onto the two clothes-pegs. The fixed part of the core, with the winding, is glued into a hole in the base of a plastic box.
 |
 |
Assembly hints:
The two halves of the core must clip together
without gaps. Here's how to do it.
- Glue and screw the two clothes-pegs to the base of the plastic box (use a solvent glue). Keep the clothes-pegs lined up by pushing a drill through the middle of both springs.
- Glue the fixed part of the core into the hole in the box (with the winding already in place). use quick-setting epoxy. Make sure that the core is square and level.
- Glue and screw the fibreglass sheet to the other side of the clothes-pegs (solvent glue). Insert the other half of the core into the hole to make sure it will locate correctly.
- Insert a spacer between the jaws of both clothes-pegs to open them up, so that the fibreglass sheet is parallel to the base of the box (see photo above).
- Locate the other half of the core exactly on top of the part with the
winding, and epoxy it to the fibreglass sheet.
Make absolutely sure that the two parts of the core will close together with no gaps. While the epoxy is still soft, remove the spacer and check that everything lines up OK. (Do not allow full spring pressure until the epoxy has completely set.)
2. Circuit Description
3. Construction
4. Calibration and Use
5. Alternative Construction